When it comes to concrete construction, accurate cost estimation is crucial. Whether you’re a seasoned contractor or just starting, understanding how concrete cost estimate can make the difference between a profitable project and one that eats into your budget, this guide will walk you through the essential steps and considerations for estimating concrete costs effectively.
Understanding the Basics of Concrete Estimate
Concrete cost estimation is not just about calculating the price of materials. It involves considering a wide range of factors, including labor, equipment, overhead, and profitability. The goal is to create an accurate estimate that reflects the total cost of the project, from start to finish.
Key Steps to Prepare a Concrete Cost Estimate
1. Outline the Project Scope
Begin by creating a rough outline of the area where you plan to pour concrete. This step is essential as it helps in visualizing the project and identifying all necessary components.
2. Measure the Dimensions
Record the length, width, and height of the structure on paper. Accurate measurements are critical because they directly influence the amount of concrete needed.
3. Calculate the Surface Area
Multiply the length by the width to determine the surface area. This figure is vital for calculating the volume of concrete required.
4. Determine the Depth
Decide on the depth of the concrete slab. The depth can vary depending on the project requirements, but it’s usually between 4 to 6 inches for residential and commercial projects.
5. Factor in Labor and Equipment
Labor costs include the time it takes to set up forms and complete the finishing touches. Equipment costs should also be factored in, especially if specialized machinery is required.
Critical Considerations for Accurate Concrete Cost Estimate
1. Project Suitability
Before diving into a project, evaluate whether it aligns with your company’s expertise. If your specialty is standard concrete work, taking on specialized projects like pavements or pump and fill jobs might not be the best fit.
2. Review Plans for Unusual Requirements
Carefully examine the project plans for any unusual requirements, such as specific materials or labor skills. These can significantly impact the overall cost and should be accounted for in the estimate.
3. Check Concrete Type and Quantity
Verify the type of concrete required for the project, such as whether it’s 3,000 or 5,000 PSI. The strength of the concrete influences its cost, so this is a crucial factor to consider.
4. Account for Special Materials
If the project requires colored concrete, reinforcing fibers, or other uncommon materials, make sure these are included in your estimate. Special materials often come with additional handling requirements and costs.
5. Recheck Your Estimate
After completing your initial estimate, take a break and then recheck your calculations. This helps ensure accuracy and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
Calculating Concrete Slab Costs

1. Determine the Thickness
The thickness of the slab is a crucial factor. For a standard residential or commercial project, a thickness of 4 inches is commonly used.
2. Measure the Surface Area
Multiply the length by the width of the slab to determine the surface area.
3. Convert Thickness to Feet
If the thickness is given in inches, convert it to feet for easier calculation.
4. Calculate the Volume in Cubic Feet
Multiply the length, width, and thickness to get the volume in cubic feet.
5. Estimate Material Costs
Contact your suppliers to get the cost of materials. This will include not only the concrete but also any reinforcing materials like rebar or mesh.
Bidding on Concrete Jobs
When preparing a bid for a concrete job, follow these steps:
1. Discuss Client Goals and Budget
Understanding the client’s objectives and budget helps tailor your bid to their needs.
2. Calculate Material and Labor Costs
Use the steps outlined above to estimate material and labor costs accurately.
3. Decide on Profit Margin
Determine an appropriate profit margin and adjust your bid accordingly.
Additional Considerations
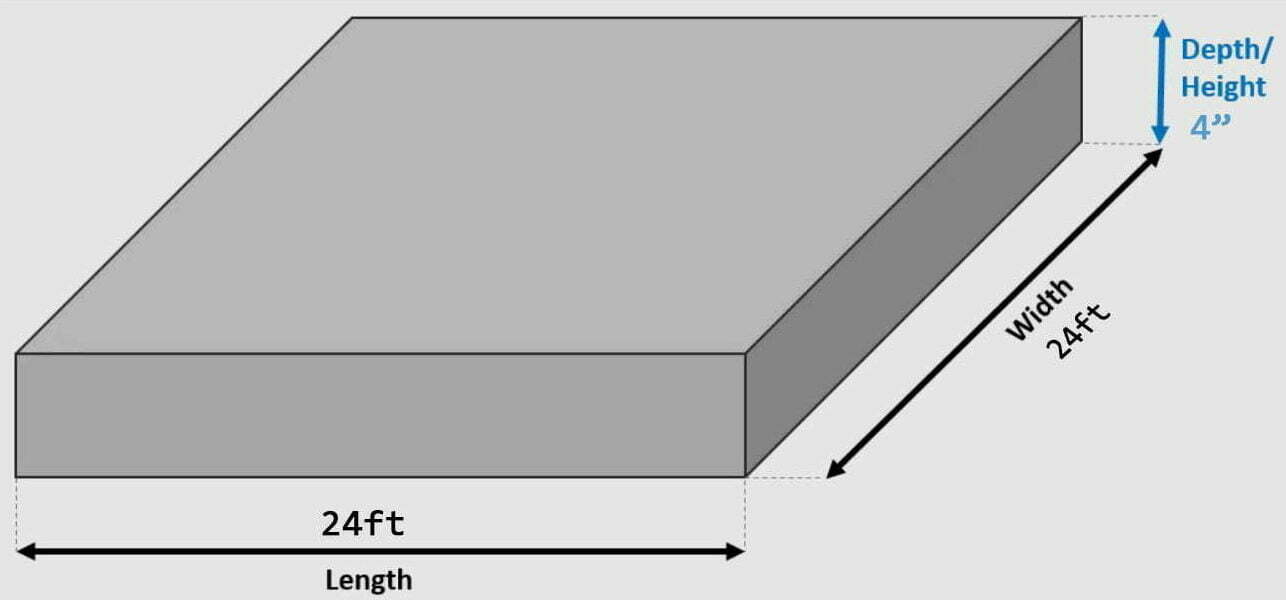
- Garage Slabs: A typical 24×24 garage slab costs between $3,057 and $5,944, depending on the thickness and reinforcement.
- Concrete Bags: It takes about 45 bags of 80lb Quikrete Concrete Mix to make one cubic yard of concrete.
Conclusion
Concrete cost estimation is a complex but essential part of any construction project. By following these guidelines and thoroughly checking your work, you can ensure that your estimates are accurate and profitable. Whether pouring a simple patio or tackling a more complex project, accurate cost estimation is the key to success.



